
- Subject:
- Psychology
- Social Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017


Background There is increasing interest to make primary data from published research publicly available. We aimed to assess the current status of making research data available in highly-cited journals across the scientific literature. Methods and Results We reviewed the first 10 original research papers of 2009 published in the 50 original research journals with the highest impact factor. For each journal we documented the policies related to public availability and sharing of data. Of the 50 journals, 44 (88%) had a statement in their instructions to authors related to public availability and sharing of data. However, there was wide variation in journal requirements, ranging from requiring the sharing of all primary data related to the research to just including a statement in the published manuscript that data can be available on request. Of the 500 assessed papers, 149 (30%) were not subject to any data availability policy. Of the remaining 351 papers that were covered by some data availability policy, 208 papers (59%) did not fully adhere to the data availability instructions of the journals they were published in, most commonly (73%) by not publicly depositing microarray data. The other 143 papers that adhered to the data availability instructions did so by publicly depositing only the specific data type as required, making a statement of willingness to share, or actually sharing all the primary data. Overall, only 47 papers (9%) deposited full primary raw data online. None of the 149 papers not subject to data availability policies made their full primary data publicly available. Conclusion A substantial proportion of original research papers published in high-impact journals are either not subject to any data availability policies, or do not adhere to the data availability instructions in their respective journals. This empiric evaluation highlights opportunities for improvement.

Currently, there is a growing interest in ensuring the transparency and reproducibility of the published scientific literature. According to a previous evaluation of 441 biomedical journals articles published in 2000–2014, the biomedical literature largely lacked transparency in important dimensions. Here, we surveyed a random sample of 149 biomedical articles published between 2015 and 2017 and determined the proportion reporting sources of public and/or private funding and conflicts of interests, sharing protocols and raw data, and undergoing rigorous independent replication and reproducibility checks. We also investigated what can be learned about reproducibility and transparency indicators from open access data provided on PubMed. The majority of the 149 studies disclosed some information regarding funding (103, 69.1% [95% confidence interval, 61.0% to 76.3%]) or conflicts of interest (97, 65.1% [56.8% to 72.6%]). Among the 104 articles with empirical data in which protocols or data sharing would be pertinent, 19 (18.3% [11.6% to 27.3%]) discussed publicly available data; only one (1.0% [0.1% to 6.0%]) included a link to a full study protocol. Among the 97 articles in which replication in studies with different data would be pertinent, there were five replication efforts (5.2% [1.9% to 12.2%]). Although clinical trial identification numbers and funding details were often provided on PubMed, only two of the articles without a full text article in PubMed Central that discussed publicly available data at the full text level also contained information related to data sharing on PubMed; none had a conflicts of interest statement on PubMed. Our evaluation suggests that although there have been improvements over the last few years in certain key indicators of reproducibility and transparency, opportunities exist to improve reproducible research practices across the biomedical literature and to make features related to reproducibility more readily visible in PubMed.

Why do we need a 'Good' Resume? We do not get a job just by sending a good one, rather we get a call for the Interview. This is what we need to remember.
I am no one to give policy statement on Resume Making. None of us can dictate a perfect resume. However, it is not a discouragement to anyone. We need to make a good one, which earns a call for the interview. The employers may not be looking at the quality of paper, but they are more keen to know what possibilities you carry. The Resume/CV you send is a 'selling document'. You sell your skills and in this barter system, you get an opportunity to work with the skills and expertise you have demonstrated.

Many of today's popular sports are based around the use of balls, yet none of the balls are completely alike. In fact, they are all designed with specific characteristics in mind and are quite varied. Students investigate different balls' abilities to bounce and represent the data they collect graphically.
abstract

A Guidebook for Optimizing Learning Contexts
Short Description:
Students enrolled in an undergraduate seminar in Educational Psychology each wrote three essays on how course content may apply to a learning context of their choice. Course content included Cognition, Self and Identity, Motivation, and Metacognitive Self Regulation. Learning contexts to which this material is applied span Early Childhood Education, Creative Writing, Math, Cheer Coaching, School Counseling, and Occupational Therapy.
Long Description:
In the summer of 2019, I entered into a teaching swap. An early career orchestra teacher gave me beginning guitar lessons and I created for her a tailored seminar in educational psychology topics selected just for her. After her first year on the job, she realized she had many questions about students related to cognition, identity, and motivation that were not addressed in her teacher-preparation coursework. The swap ended up being of value to both of us. And really, what a delightful way to spend a summer! We both love teaching and learning and music and shared our expertise with each other for nearly two months. As the next school year started, my friend felt that what covered was really beneficial. How wonderful.
As such, early in January 2020, my reading list and discussion notes in hand, I developed a proposal for a new course reflecting that summer “seminar” experience. I pitched the course to music education majors, and described it as an extension to the standard educational psychology coursework they were required to take. That is, I pitched it as an elective. By the time students began to register for summer and fall 2020 courses, the corona-virus had taken hold of our lives, and the format of summer school had to change. My thinking about the course had changed too. Rather than limit enrolled students to one kind of teaching application, I realized that we would all get more out of the course if it were expanded to include a variety of teaching (or coaching, mentoring, or therapy) experiences. And with that, enough students enrolled in the course to make it a “go.”
Before the course began I polled students about their interests and I made sure to include at least one reading that would be clearly related to their particular interests and experiences. Over the span of 4 weeks, the students and I dove in to the course content undaunted by our Zoom connection. Enrolled students entered with a variety of interests. Some had extensive teaching experience already, others had none. All, of course, had quite a bit of experience as students though, and so as the class rolled along, while learning new content we also learned about how it might apply to many different teaching and learning contexts. It really was a fantastic course.
In the chapters that follow, you will see how each student took the course material and applied it to a context of their own choosing. Each section is comprised of three chapters, all tailored to the context: Early Childhood Education, Creative Writing, Math, Cheer Coaching, School Counseling, and Occupational Therapy. While the authors are undergraduates, the knowledge they’ve gained and shared here is sound. Readers can trust that the recommendations are couched in empirical research and theory. We hope that you enjoy reading and that you find it useful as well! And if you want to read further yourselves, you will find the class reading list in the appendix.
Word Count: 32121
(Note: This resource's metadata has been created automatically by reformatting and/or combining the information that the author initially provided as part of a bulk import process.)

This lesson unit is intended to help teachers assess how well students are able to: solve linear equations in one variable with rational number coefficients; collect like terms; expand expressions using the distributive property; and categorize linear equations in one variable as having one, none, or infinitely many solutions. It also aims to encourage discussion on some common misconceptions about algebra.
Completion of the study of the first year sequence of basic skills. This course was formerly known as Spanish 101. Prerequisite: none. Students will learn vocabulary related to greetings and farewells, courtesy expressions, college courses, professions, family relationships, pastimes, city places, numbers, days of the week, months and how to tell time. Students learn grammatical structures that support sentence formation, such as nouns and articles; descriptive and possessive adjectives; the present tense of ser, estar, tener, venir, ir, ver and oÍr; the present tense of regular _ar, _er and _ir verbs; stem changing verbs (e-ie, e-i and o-ue); verbs with irregular yo forms (hacer, poner, salir, suponer and traer); and question formation.

For teaching staff
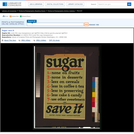
Poster showing a list of ways to save sugar. Text continues: 1. none on fruits; 2. none in desserts; 3. less on cereals; 4. less in coffee and tea; 5. less in preserving; 6. less cake & candy; 7. use other sweeteners. United States Food Administration.
This is, bar none, the greatest video Khan Academy has ever made, although I may be slightly overstating that. Learn how to master this style by following along.

Authors: Erin M. Buchanan, Tabetha Hopke, Simon DonaldsonEducational use: Use these materials to teach an undergraduate statistics course with a primary social science focus.Abstract: Want to teach an undergraduate statistics course using open source materials? You have come to the right place! A complete set of how-to guides for JASP, learning objectives, and pre-made course materials for you to use in your class.Audience: Educators, Students who need extra how-to helpLevel: IntroductoryPrerequisites: None

This unit initiates a discussion about the importance of recognizing faults in relation to modern societal infrastructure. Students consider the types of infrastructure necessary to support a modern lifestyle, especially for people living in population centers. Students also explore how key infrastructure such as aqueducts, power lines, or oil/gas pipelines, which traverse large distances, may also be susceptible to damage by earthquakes well away from the population centers. Additionally, earthquakes can occur in regions where none have occurred in recorded history. The ability to recognize and evaluate the potential for damage to key infrastructure that are near or cross a fault can be used, in turn, to classify and ultimately predict the most and least likely locations for damage, and to make suggestions for minimizing future impacts.
Show more about Online Teaching suggestions
Hide
Online-ready: The exercise is electronic and could be done individually or in small online groups (using the Google Earth rather than printable files). Lecture can be done in synchronous or asynchronous online format, although synchronous would allow better discussions of societal impacts of earthquakes.
(Note: this resource was added to OER Commons as part of a batch upload of over 2,200 records. If you notice an issue with the quality of the metadata, please let us know by using the 'report' button and we will flag it for consideration.)
The Journal Impact Factor (JIF) was originally designed to aid libraries in deciding which journals to index and purchase for their collections. Over the past few decades, however, it has become a relied upon metric used to evaluate research articles based on journal rank. Surveyed faculty often report feeling pressure to publish in journals with high JIFs and mention reliance on the JIF as one problem with current academic evaluation systems. While faculty reports are useful, information is lacking on how often and in what ways the JIF is currently used for review, promotion, and tenure (RPT). We therefore collected and analyzed RPT documents from a representative sample of 129 universities from the United States and Canada and 381 of their academic units. We found that 40% of doctoral, research-intensive (R-type) institutions and 18% of master’s, or comprehensive (M-type) institutions explicitly mentioned the JIF, or closely related terms, in their RPT documents. Undergraduate, or baccalaureate (B-type) institutions did not mention it at all. A detailed reading of these documents suggests that institutions may also be using a variety of terms to indirectly refer to the JIF. Our qualitative analysis shows that 87% of the institutions that mentioned the JIF supported the metric’s use in at least one of their RPT documents, while 13% of institutions expressed caution about the JIF’s use in evaluations. None of the RPT documents we analyzed heavily criticized the JIF or prohibited its use in evaluations. Of the institutions that mentioned the JIF, 63% associated it with quality, 40% with impact, importance, or significance, and 20% with prestige, reputation, or status. In sum, our results show that the use of the JIF is encouraged in RPT evaluations, especially at research-intensive universities, and indicates there is work to be done to improve evaluation processes to avoid the potential misuse of metrics like the JIF.
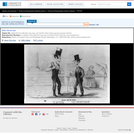
Another cartoon relating to the dispute between the United States and Great Britain over the northern boundary of American territory in Oregon. Opinion was sharply divided between support for a compromise claim of territory as far north as the forty-ninth parallel, and those who went for the more expansive 4.40 boundary. Palmer has two Irish immigrants disputing the issue. Wearing overalls, suspenders, boots, and stovepipe hats, the characters stand outside the Bowery Theater. (The Bowery section of New York City was known for its concentration of working-class Irish.) The man on the left says, "Ike! say the 49th & let's settle it amercably." The other responds, "No Sir-ree I goes for the hull of Oregon or none--I do & don't do nor-thin else." In the background, a woman sells apples and what look like nuts at a table. Behind her the theater's billboard advertises "Great Attraction. Adelgis. J.R. Scott. Cony & Blanchard."|Entered . . . 1846 by Thomas Odham.|Lith. F. & S. Palmer - 43 Ann Street N. York|Signed: F.P. (Frances Palmer).|The Library's impression was deposited for copyright on April 25, 1846.|Title appears as it is written on the item.|Weitenkampf, p. 86.|Forms part of: American cartoon print filing series (Library of Congress)|Published in: American political prints, 1766-1876 / Bernard F. Reilly. Boston : G.K. Hall, 1991, entry 1846-4.

I intend this book to be, firstly, a introduction to calculus based on the hyperreal number system. In other words, I will use infinitesimal and infinite numbers freely. Just as most beginning calculus books provide no logical justification for the real number system, I will provide none for the hyperreals. The reader interested in questions of foundations should consult books such as Abraham Robinson's Non-standard Analysis or Robert Goldblatt's Lectures on the Hyperreals. Secondly, I have aimed the text primarily at readers who already have some familiarity with calculus. Although the book does not explicitly assume any prerequisites beyond basic algebra and trigonometry, in practice the pace is too fast for most of those without some acquaintance with the basic notions of calculus.

Current attempts at methodological reform in sciences come in response to an overall lack of rigor in methodological and scientific practices in experimental sciences. However, some of these reform attempts suffer from the same mistakes and over-generalizations they purport to address. Considering the costs of allowing false claims to become canonized, we argue for more rigor and nuance in methodological reform. By way of example, we present a formal analysis of three common claims in the metascientific literature: (a) that reproducibility is the cornerstone of science; (b) that data must not be used twice in any analysis; and (c) that exploratory projects are characterized by poor statistical practice. We show that none of these three claims are correct in general and we explore when they do and do not hold.

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"Differential abundance analysis (DAA) is a key statistical method for comparing microbiome compositions under different conditions, such as health vs. disease. However, DAA is complicated by the use of relative, rather than absolute, abundance values and by a high risk of false positives, or detection of significant effects when there aren’t any. In addition, the existing DAA tools can produce very divergent results from the same data, making it difficult to select the best tool. To provide guidance, a new study comprehensively evaluated the currently available tools with simulations based on real data. The researchers found that none of the tools were simultaneously robust, powerful, and flexible. Therefore, they concluded that none were suitable for blind application to real microbiome datasets. To build a better path forward, the researchers designed a new tool, ZicoSeq that drew on the strengths of the other available DAA methods while addressing their major limitations..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.