This OER is about the basic of first law of thermodyanamics.
- Subject:
- Career and Technical Education
- Material Type:
- Lecture Notes
- Date Added:
- 07/23/2016

This OER is about the basic of first law of thermodyanamics.

This course introduces thermodynamic principles; open and closed systems representative of engineering problems; and first and second law of thermodynamics with applications to engineering systems and design. Topics include: thermodynamic concepts, thermodynamic properties, the first law of thermodynamics, first law analysis for a control volume, the second law of thermodynamics, entropy, and second law analysis for a control volume.
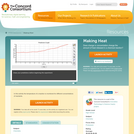
In this activity the temperature of a reaction is monitored for different concentrations of reactants.

This course discusses the selection and evaluation of commercial and naval ship power and propulsion systems. It will cover the analysis of propulsors, prime mover thermodynamic cycles, propeller-engine matching, propeller selection, waterjet analysis, and reviews alternative propulsors. The course also investigates thermodynamic analyses of Rankine, Brayton, Diesel, and Combined cycles, reduction gears and integrated electric drive. Battery operated vehicles and fuel cells are also discussed. The term project requires analysis of alternatives in propulsion plant design for given physical, performance, and economic constraints. Graduate students complete different assignments and exams.

Material covered in this course includes the following topics:
Laws of thermodynamics: general formulation and applications to mechanical, electromagnetic and electrochemical systems, solutions, and phase diagrams
Computation of phase diagrams
Statistical thermodynamics and relation between microscopic and macroscopic properties, including ensembles, gases, crystal lattices, phase transitions
Applications to phase stability and properties of mixtures
Computational modeling
Interfaces
This course was also taught as part of the Singapore-MIT Alliance (SMA) programme as course number SMA 5111 (Materials at Equilibrium).

The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution describes the distribution of speeds among the particles in a sample of gas at a given temperature. The distribution is often represented graphically, with particle speed on the x-axis and relative number of particles on the y-axis. Created by Sal Khan.

This activity is an inquiry lesson where students learn how to accurately read a thermometer and then set up an investigation to compare the temperatures of different materials or locations.

How do microwaves heat up your coffee? Adjust the frequency and amplitude of microwaves. Watch water molecules rotating and bouncing around. View the microwave field as a wave, a single line of vectors, or the entire field.

How do microwaves heat up your coffee? Adjust the frequency and amplitude of microwaves. Watch water molecules rotating and bouncing around. View the microwave field as a wave, a single line of vectors, or the entire field.
Modelling is about understanding the nature: our world, ourselves and our work. Everything that we observe has a cause (typically several) and has the effect thereof. The heart of modelling lies in identifying, understanding and quantifying these cause-and-effect relationships.
A model can be treated as a (selective) representation of a system. We create the model by defining a mapping from the system space to the model space, thus we can map system state and behaviour to model state and behaviour. By defining the inverse mapping, we may map results from the study of the model back to the system. In this course, using an overarching modelling paradigm, students will become familiar with several instances of modelling, e.g., mechanics, thermal dynamics, fluid mechanics, etc.

This type of physics course can easily seem to the student like a random grab-bag of topics, consisting of everything that didn’t fit in the earlier semesters on mechanics and electromagnetism. But there is a clear organizing principle for most of what we’ll be studying. It has to do with two surprising facts about time. In particular, one of these facts leads us to the conclusion that light and matter can’t really be made of particles, as envisioned by Isaac Newton’s grand vision of the universe — they must be made of waves.

This site provides a free physics textbook that tells the story of how it became possible, after 2500 years of exploration, to answer such questions. The book is written for the curious: it is entertaining, surprising and challenging on every page. With little mathematics, starting from observations of everyday life, the text explores the most fascinating parts of mechanics, thermodynamics, special and general relativity, electrodynamics, quantum theory and modern attempts at unification. The essence of these fields is summarized in the most simple terms. For example, the text presents modern physics as consequence of the notions of minimum entropy, maximum speed, maximum force, minimum change of charge and minimum action.

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"Notch signaling is the key to many binary decisions metazoan cells make during development. Downstream signals from Notch trigger transcriptional remodeling that resolves dichotomies like differentiation between developmental cell fates. In the "Notch on" state, the Notch intracellular domain (NICD) relocates to the nucleus and binds to the protein RBPJ. While Notch activation is well studied, the transition to the "Notch off" state, where NICD and RBPJ dissociate, is not well understood. Recent research using phylogenetic analysis, computational biochemistry, and in vitro experiments suggests that heat flux is an important regulator of Notch signaling. The researchers determined that NICD senses temperature changes through its ankyrin domain. The ankyrin domain is highly conserved across species and contains β-hairpins enriched for charged amino acids. These charged amino acids amplify destabilizing electrostatic interactions, making the domain vulnerable to heat destruction..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.

Students will use science skills of observing, describing and measuring in the context of Making Ice Cream. Students will understand the concept that physical properties can change.

Introduction to pressure-volume diagrams.

Introduction to pressure-volume diagrams, part 2.

This course covers the basics of general relativity, standard big bang cosmology, thermodynamics of the early universe, cosmic background radiation, primordial nucleosynthesis, basics of the standard model of particle physics, electroweak and QCD phase transition, basics of group theory, grand unified theories, baryon asymmetry, monopoles, cosmic strings, domain walls, axions, inflationary universe, and structure formation.
The People's Physics Book v3 is intended to be used as one small part of a multifaceted strategy to teach physics conceptually and mathematically
In this course, you will learn about phase relations as applied to oil and/or gas reservoir processes, enhanced oil recovery, gas pipeline transportation, natural gas processing and liquefaction, and other problems in petroleum production. The primary objective of the course is to apply the thermodynamics of phase equilibrium to the framework for phase behavior modeling of petroleum fluids. The focus of the course will be on equilibrium thermodynamics and its relevance to phase behavior predictions and phase equilibrium data description. We will attempt to apply phase behavior principles to petroleum production processes of practical interest, especially natural gas condensate systems.

This course discusses phase transitions in Earth's interior. Phase transitions in Earth materials at high pressures and temperatures cause the seismic discontinuities and affect the convections in the Earth's interior. On the other hand, they enable us to constrain temperature and chemical compositions in the Earth's interior. However, among many known phase transitions in mineral physics, only a few have been investigated in seismology and geodynamics. This course reviews important papers about phase transitions in mantle and core materials.