
16 Results


Biology is designed for multi-semester biology courses for science majors. It is grounded on an evolutionary basis and includes exciting features that highlight careers in the biological sciences and everyday applications of the concepts at hand. To meet the needs of today’s instructors and students, some content has been strategically condensed while maintaining the overall scope and coverage of traditional texts for this course. Instructors can customize the book, adapting it to the approach that works best in their classroom. Biology also includes an innovative art program that incorporates critical thinking and clicker questions to help students understand—and apply—key concepts.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
- Date Added:
- 08/22/2012
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Unit of Study
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College

- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017
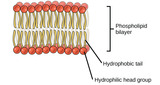
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the four major types of lipidsExplain the role of fats in storing energyDifferentiate between saturated and unsaturated fatty acidsDescribe phospholipids and their role in cellsDefine the basic structure of a steroid and some functions of steroidsExplain the how cholesterol helps to maintain the fluid nature of the plasma membrane
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the four major types of lipidsExplain the role of fats in storing energyDifferentiate between saturated and unsaturated fatty acidsDescribe phospholipids and their role in cellsDefine the basic structure of a steroid and some functions of steroidsExplain the how cholesterol helps to maintain the fluid nature of the plasma membrane
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Author:
- Tina B. Jones
- Date Added:
- 09/03/2019

In this activity, students will have the opportunity to give nutritional advice to their peers and recommend a day of healthy meals to a visiting international student.
- Subject:
- Arts and Humanities
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Date Added:
- 03/11/2019

This presentation focus on which role nutrition plays in developing diabetes and how obesity affects diabetes development. Obesity and weight gain dramatically increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. But it’s not only the total calorie intake and the BMI that counts, so does the distribution between fat, protein and carbohydrates, in other words the composition of nutritions. In continuation of this it will be discussed how a restricting intake of carbohydrates might be the way to reduce or even eliminate the use of medication in diabetes treatments.
Narrator: Richard Steed.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Health, Medicine and Nursing
- Material Type:
- Lecture
- Provider:
- University of Copenhagen Department of Biomedical Science
- Provider Set:
- Diabetes - The Essential Facts
- Author:
- Associate Professor Signe Sørensen Torekov
- MD Nicolai Wewer Albrechtsen
- Professor Arne Astrup
- Professor Jens Juul Holst
- Professor Venkat Narayan
- Date Added:
- 01/07/2016
In this activity, students will have the opportunity to give nutritional advice to their peers and recommend a day of healthy meals to a visiting international student.
- Subject:
- Arts and Humanities
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Date Added:
- 09/14/2018
In this activity, students will have the opportunity to give nutritional advice to their peers and recommend a day of healthy meals to a visiting international student.
- Subject:
- Arts and Humanities
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Date Added:
- 06/11/2018

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"Too much dietary fat can be bad for our health. Chronic high lipid intake results in the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver, causing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). One contributor to NAFLD is the inhibition of a process called autophagy, where the body’s cells clean up intracellular components that are damaged or no longer needed. Unfortunately, how autophagy inhibition results in NAFLD is unknown. A recent study aimed to determine what molecular pathways inhibit autophagy to cause NAFLD. Using yellow catfish as a model, they compared the effects of regular and high-lipid diets on autophagy and lipid metabolism. RNA sequencing showed that a high-fat diet altered the expression of many genes associated with lipid metabolism and autophagy. A pair of proteins, FXR and CREB, served as a switch to regulate these changes, maintaining a proper fatty acid balance and protecting cells from lipid-induced damage..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Reading
- Provider:
- Research Square
- Provider Set:
- Video Bytes
- Date Added:
- 06/23/2020

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"Increased blood flow to the uterus during pregnancy is essential to the health of both mother and baby But the cellular processes that promote blood flow during pregnancy aren’t fully understood Now, researchers have discovered that fat surrounding blood vessels in the uterus plays a key role In pregnant rats, uterine blood flow was up to 3 times higher than in non-pregnant rats But blood flow plummeted when fat tissue was removed from the uterus of pregnant rats Interestingly, tests on isolated vessels demonstrated that fat tissue-shrinking factors could be at play which seems counterintuitive because narrow vessels generally mean low blood flow One explanation is that isolating tissue from its natural surroundings could produce changes not observed in a live animal Future studies will explore this apparent contradiction and hopefully reveal the role of fat tissue in human pregnancy Osikoya et al..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.
- Subject:
- Anatomy/Physiology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Reading
- Provider:
- Research Square
- Provider Set:
- Video Bytes
- Date Added:
- 09/20/2019

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"Today's obesity epidemic is driven by increased consumption of foods that are high in fat and low in soluble fiber, which alters the makeup of the gut microbiome. These changes also vary by age and sex, causing differences in susceptibility to obesity. Unfortunately, most animal studies compare diets that vary in both fat and fiber, making it difficult to determine which has an effect. Now, a new study suggests that fiber could play the more prominent role. The authors of the study profiled the microbial community in mice fed diets varying in either fiber or fat, but not both. 16S rRNA sequencing revealed that changes in fiber accounted for most of the variance in microbes. While these changes were age- and sex-specific, they were not dependent on dietary fat. Although further studies are needed to fully understand these effects, the results suggest that in animal obesity studies, the choice of control diet matters..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Nutrition
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Reading
- Provider:
- Research Square
- Provider Set:
- Video Bytes
- Date Added:
- 04/16/2020

This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"One promising way to fight obesity and its complications is to keep fat tissue in the body from expanding But as simple as that sounds, researchers aren’t yet sure where to start While the antioxidant-regulating protein Nrf2 is known to play a role in the development of fat tissue activating or de-activating Nrf2 appears to have the same fat-reducing effect Now, researchers could have a better handle on Nrf2’s role Through genetic and protein analyses, one team has discovered that Nrf2 works in concert with the receptor PDGFRα PDGFRα is critical for the development of certain organs and tissues, including body fat The team found that, in the absence of the adaptor protein Nck1, PDGFRα activation and Nrf2 expression are increased Activating the PDGFRα-Nrf2 pathway in mice impaired bone marrow cells’ ability to turn into fat These findings mirror those obtained by the same team for cells gathered from white fat tissue in mice Though it’s not yet clear how the results will carry o.."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Reading
- Provider:
- Research Square
- Provider Set:
- Video Bytes
- Date Added:
- 04/24/2020

The aim of this presentation is to expand the students’ knowledge about industrially produced trans fat (artificial trans fat). We will focus on how and why we produce trans fat. Furthermore, we will focus on the health consequences of eating trans fat.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Health, Medicine and Nursing
- Life Science
- Nutrition
- Material Type:
- Lecture
- Provider:
- University of Copenhagen
- Provider Set:
- The New Nordic Diet - From Gastronomy to Health
- Author:
- Chief Physician Steen Stender
- Date Added:
- 01/07/2016
Humans are omnivores (able to survive on many different foods). The omnivore’s dilemma is to identify foods that are healthy and avoid poisons. Taste and smell cooperate to solve this dilemma. Stimuli for both taste and smell are chemicals. Smell results from a biological system that essentially permits the brain to store rough sketches of the chemical structures of odor stimuli in the environment. Thus, people in very different parts of the world can learn to like odors (paired with calories) or dislike odors (paired with nausea) that they encounter in their worlds. Taste information is preselected (by the nature of the receptors) to be relevant to nutrition. No learning is required; we are born loving sweet and hating bitter. Taste inhibits a variety of other systems in the brain. Taste damage releases that inhibition, thus intensifying sensations like those evoked by fats in foods. Ear infections and tonsillectomies both can damage taste. Adults who have experienced these conditions experience intensified sensations from fats and enhanced palatability of high-fat foods. This may explain why individuals who have had ear infections or tonsillectomies tend to gain weight.
- Subject:
- Psychology
- Social Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Provider:
- Diener Education Fund
- Provider Set:
- Noba
- Author:
- Derek Snyder
- Linda Bartoshuk
- Date Added:
- 11/02/2022