Learn About the National Network
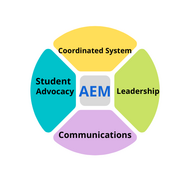
(View Complete Item Description)Learn About the National Network [Version en Español] The ADA National Network provides information, guidance and training on how to implement the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in order to support the mission of the ADA to “assure equality of opportunity, full participation, independent living, and economic self-sufficiency for individuals with disabilities.” Funded by the National Institute on Disability, Independent Living, and Rehabilitation Research (NIDILRR), the network consists of 10 Regional ADA Centers located throughout the United States and an ADA Knowledge Translation Center (ADAKTC). Each Regional ADA Center focuses on its region’s unique needs. This regional focus is critical to ensuring that ADA National Network services meet the needs of a diversity of populations and stakeholders throughout the country.
Material Type: Primary Source