31 Results


This resource is a video abstract of a research paper created by Research Square on behalf of its authors. It provides a synopsis that's easy to understand, and can be used to introduce the topics it covers to students, researchers, and the general public. The video's transcript is also provided in full, with a portion provided below for preview:
"In the absence of oxygen, some prokaryotes can degrade organic matter via anaerobic digestion. This occurs in natural settings, like wetlands, and industrial ones, like wastewater treatment or biogas production. But what about viruses? Bacteriophages can impact their hosts’ community structure through selective pressure and have been used to influence microbial communities, such as through pathogen control. A recent study examined the virome of anaerobic digestion communities undergoing prophage- inducing environmental stresses. The virome was almost entirely composed of tailed bacteriophages of the order Caudovirales. Metagenome reconstruction revealed 1,092 viral genomes and 120 prokaryotic genomes, and over half of the prokaryotic genomes contained a provirus in their genomic sequence. In general, species of viruses and prokaryotes could be grouped by having similar reactions to stressors. Archaea had the most pronounced reactions to stressors and featured behaviors unique to those species..."
The rest of the transcript, along with a link to the research itself, is available on the resource itself.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Diagram/Illustration
- Reading
- Provider:
- Research Square
- Provider Set:
- Video Bytes
- Date Added:
- 04/14/2023
In this new video we look at the basics of bacteria. We look at their classifications, sizes, shapes and how they reproduce. This video is intended to be a primer on bacteria. We will go into more details as we progress in this series.
--------------
Visit Us On The Internet:
-YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/mrfordsclass
-Twitter: https://twitter.com/mrfordsclass
-Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/mrfordsclasslearning
-Google+: https://plus.google.com/+mrfordsclass/posts
-Instagram: http://instagram.com/mrfordsclasslearning
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Lecture
- Provider:
- Mr. Ford's Class
- Author:
- Scott Ford
- Date Added:
- 12/06/2014
Students construct paper recombinant plasmids to simulate the methods genetic engineers use to create modified bacteria. They learn what role enzymes, DNA and genes play in the modification of organisms. For the particular model they work on, they isolate a mammal insulin gene and combine it with a bacteria's gene sequence (plasmid DNA) for production of the protein insulin.
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Engineering
- Genetics
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Provider:
- TeachEngineering
- Provider Set:
- TeachEngineering
- Author:
- Kimberly Anderson
- Matthew Zelisko
- Date Added:
- 09/18/2014

Biology is designed for multi-semester biology courses for science majors. It is grounded on an evolutionary basis and includes exciting features that highlight careers in the biological sciences and everyday applications of the concepts at hand. To meet the needs of today’s instructors and students, some content has been strategically condensed while maintaining the overall scope and coverage of traditional texts for this course. Instructors can customize the book, adapting it to the approach that works best in their classroom. Biology also includes an innovative art program that incorporates critical thinking and clicker questions to help students understand—and apply—key concepts.
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
- Date Added:
- 08/22/2012
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Unit of Study
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
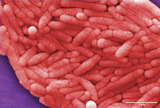
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Identify bacterial diseases that caused historically important plagues and epidemicsDescribe the link between biofilms and foodborne diseasesExplain how overuse of antibiotic may be creating “super bugs”Explain the importance of MRSA with respect to the problems of antibiotic resistance
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017
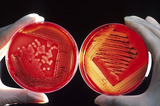
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Explain the need for nitrogen fixation and how it is accomplishedIdentify foods in which prokaryotes are used in the processingDescribe the use of prokaryotes in bioremediationDescribe the beneficial effects of bacteria that colonize our skin and digestive tracts
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017

- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the evolutionary history of prokaryotesDiscuss the distinguishing features of extremophilesExplain why it is difficult to culture prokaryotes
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Identify the macronutrients needed by prokaryotes, and explain their importanceDescribe the ways in which prokaryotes get energy and carbon for life processesDescribe the roles of prokaryotes in the carbon and nitrogen cycles
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017
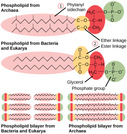
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the basic structure of a typical prokaryoteDescribe important differences in structure between Archaea and Bacteria
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Unit of Study
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College

- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017
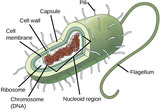
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Name examples of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organismsCompare and contrast prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cellsDescribe the relative sizes of different kinds of cellsExplain why cells must be small
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017
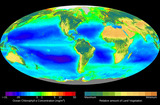
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Author:
- Tina B. Jones
- Date Added:
- 08/16/2019

- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017
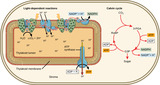
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the Calvin cycleDefine carbon fixationExplain how photosynthesis works in the energy cycle of all living organisms
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Author:
- Tina B. Jones
- Date Added:
- 08/16/2019

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the Calvin cycleDefine carbon fixationExplain how photosynthesis works in the energy cycle of all living organisms
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Date Added:
- 07/10/2017
- Subject:
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Unit of Study
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College