This task provides Grade 3 students with modeling practice.
- Subject:
- Education
- Elementary Education
- Mathematics
- Numbers and Operations
- Material Type:
- Activity/Lab
- Assessment
- Homework/Assignment
- Date Added:
- 08/15/2018

This task provides Grade 3 students with modeling practice.
A mathematics task that involves a multi-step word problem related to addition and subtraction situations. Students are expected to model with mathematics as they complete the task. Task relates to standard 2.OA. A.1

This task has students solve a multi-step addition and subtraction problem based on a given data chart. Students are solving a variety of problem types involving addition and subtraction. This task is related to evidence statement 3.D.2 and Common Core Standard 2.OA.A.1

Students learn how 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is revolutionizing the manufacturing process. First, students learn what considerations to make in the engineering design process to print an object with quality and to scale. Students learn the basic principles of how a computer-aided design (CAD) model is converted to a series of data points then turned into a program that operates the 3D printer. The activity takes students through a step-by-step process on how a computer can control a manufacturing process through defined data points. Within this activity, students also learn how to program using basic G-code to create a wireframe 3D shapes that can be read by a 3D printer or computer numerical control (CNC) machine.
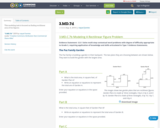
This modeling task is focused on finding rectilinear area of two figures.

This modeling task is focused on finding rectilinear area of two figures.

This task provides students practice with modeling.
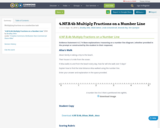
Multiplying fractions on a numberline task

This resource provides students with the opportunity to solve a multi-step contextual word problem with a degree of difficulty appropriate to Grade 4, requiring application of knowledge and skills.
This resource provides students with the opportunity to solve a multi-step contextual word problem with a degree of difficulty appropriate to Grade 4, requiring application of knowledge and skills.

This class covers the analysis and modeling of stochastic processes. Topics include measure theoretic probability, martingales, filtration, and stopping theorems, elements of large deviations theory, Brownian motion and reflected Brownian motion, stochastic integration and Ito calculus and functional limit theorems. In addition, the class will go over some applications to finance theory, insurance, queueing and inventory models.
Building on Complex Adaptive Systems theory and basic Agent Based Modeling knowledge presented in SPM4530, the Advanced course will focus on the model development process. The students are expected to conceptualize, develop and verify a model during the course, individually or in a group. The modeling tasks will be, as much as possible, based on real life research problems, formulated by various research groups from within and outside the faculty.
Study Goals The main goal of the course is to learn how to form a modeling question, perform a system decomposition, conceptualize and formalize the system elements, implement and verify the simulation and validate an Agent Based Model of a socio-technical system.

Students are introduced to measuring and identifying sources of air pollution, as well as how environmental engineers try to control and limit the amount of air pollution. In Part 1, students are introduced to nitrogen dioxide as an air pollutant and how it is quantified. Major sources are identified, using EPA bar graphs. Students identify major cities and determine their latitudes and longitudes. They estimate NO2 values from color maps showing monthly NO2 averages from two sources: a NASA satellite and the WSU forecast model AIRPACT. In Part 2, students continue to estimate NO2 values from color maps and use Excel to calculate differences and ratios to determine the model's performance. They gain experience working with very large numbers written in scientific notation, as well as spreadsheet application capabilities.
"In this module, students synthesize and generalize what they have learned about a variety of function families. They extend the domain of exponential functions to the entire real line (N-RN.A.1) and then extend their work with these functions to include solving exponential equations with logarithms (F-LE.A.4). They explore (with appropriate tools) the effects of transformations on graphs of exponential and logarithmic functions. They notice that the transformations on a graph of a logarithmic function relate to the logarithmic properties (F-BF.B.3). Students identify appropriate types of functions to model a situation. They adjust parameters to improve the model, and they compare models by analyzing appropriateness of fit and making judgments about the domain over which a model is a good fit. The description of modeling as, the process of choosing and using mathematics and statistics to analyze empirical situations, to understand them better, and to make decisions, is at the heart of this module. In particular, through repeated opportunities in working through the modeling cycle (see page 61 of the CCLS), students acquire the insight that the same mathematical or statistical structure can sometimes model seemingly different situations.
Find the rest of the EngageNY Mathematics resources at https://archive.org/details/engageny-mathematics."

(Nota: Esta es una traducción de un recurso educativo abierto creado por el Departamento de Educación del Estado de Nueva York (NYSED) como parte del proyecto "EngageNY" en 2013. Aunque el recurso real fue traducido por personas, la siguiente descripción se tradujo del inglés original usando Google Translate para ayudar a los usuarios potenciales a decidir si se adapta a sus necesidades y puede contener errores gramaticales o lingüísticos. La descripción original en inglés también se proporciona a continuación.)
"En este módulo, los estudiantes sintetizan y generalizan lo que han aprendido sobre una variedad de familias de funciones. Extienden el dominio de las funciones exponenciales a toda la línea real (n-rn.a.1) y luego extienden su trabajo con estas funciones a incluir la resolución de ecuaciones exponenciales con logaritmos (F-le.a.4). Exploran (con herramientas apropiadas) los efectos de las transformaciones en gráficos de funciones exponenciales y logarítmicas. Notan que las transformaciones en un gráfico de una función logarítmica se relacionan con el Propiedades logarítmicas (F-BF.B.3). Los estudiantes identifican tipos apropiados de funciones para modelar una situación. Ajustan los parámetros para mejorar el modelo y comparan los modelos analizando la idoneidad del ajuste y las juicios sobre el dominio sobre el cual un modelo es un buen ajuste. La descripción del modelado como, el proceso de elegir y usar matemáticas y estadísticas para analizar situaciones empíricas, comprenderlas mejor y tomar decisiones, está en el corazón de este módulo. En particular, a través de oportunidades repetidas para trabajar a través del ciclo de modelado (consulte la página 61 del CCLS), los estudiantes adquieren la idea de que la misma estructura matemática o estadística a veces puede modelar situaciones aparentemente diferentes.
Encuentre el resto de los recursos matemáticos de Engageny en https://archive.org/details/engageny-mathematics ".
English Description:
"In this module, students synthesize and generalize what they have learned about a variety of function families. They extend the domain of exponential functions to the entire real line (N-RN.A.1) and then extend their work with these functions to include solving exponential equations with logarithms (F-LE.A.4). They explore (with appropriate tools) the effects of transformations on graphs of exponential and logarithmic functions. They notice that the transformations on a graph of a logarithmic function relate to the logarithmic properties (F-BF.B.3). Students identify appropriate types of functions to model a situation. They adjust parameters to improve the model, and they compare models by analyzing appropriateness of fit and making judgments about the domain over which a model is a good fit. The description of modeling as, the process of choosing and using mathematics and statistics to analyze empirical situations, to understand them better, and to make decisions, is at the heart of this module. In particular, through repeated opportunities in working through the modeling cycle (see page 61 of the CCLS), students acquire the insight that the same mathematical or statistical structure can sometimes model seemingly different situations.
Find the rest of the EngageNY Mathematics resources at https://archive.org/details/engageny-mathematics."

Students learn how nanoparticles can be creatively used for medical diagnostic purposes. They learn about buckminsterfullerenes, more commonly known as buckyballs, and about the potential for these complex carbon molecules to deliver drugs and other treatments into the human body. They brainstorm methods to track buckyballs in the body, then build a buckyball from pipe cleaners with a fluorescent tag to model how nanoparticles might be labeled and detected for use in a living organism. As an extension, students research and select appropriate radioisotopes for different medical applications.
In this lesson, students explore the importance of albedo (or reflectivity) to penguins and the surfaces they inhabit and learn how penguin colonies may be mapped using satellites.

15.875 is a project-based course that explores how organizations can use system dynamics to achieve important goals. In small groups, students learn modeling and consulting skills by working on a term-long project with real-life managers. A diverse set of businesses and organizations sponsor class projects, from start-ups to the Fortune 500. The course focuses on gaining practical insight from the system dynamics process, and appeals to people interested in system dynamics, consulting, or managerial policy-making.

This is the second undergraduate architecture design studio, which introduces design logic and skills that enable design thinking, representation, and development. Through the lens of nano-scale machines, technologies, and phenomena, students are asked to explore techniques for describing form, space, and architecture. Exercises encourage various connotations of the "machine" and challenge students to translate conceptual strategies into more integrated design propositions through both digital and analog means.

This textbook is based on a different paradigm for organizing an engineering science core --- a systems, accounting and modeling approach --- that emphasizes the common, underlying concepts of engineering science. Although this approach is not new, as most graduate students have been struck by this idea sometime during their graduate education, its use as the organizing principle for an undergraduate curriculum is new. By focusing on the underlying concepts and stressing the similarities between subjects that are often perceived by students (and taught by faculty) as unconnected topics, this approach provides engineering students a foundational framework for recognizing and building connections as they travel through their education.